Primitive Types
byteshortintlongfloatdoublebooleanchar
Reference Types
Everything not belonging to [[#Primitive_Types.md|#Primitive_Types]] is a reference type, including arrays.
Class instantiation
When we instantiate(new) an Object (e.g. Dog, Walrus, Planet):
- Java first allocates a box of bits for each instance variable of the class and fills them with a default value (e.g. 0, null).
- The constructor then usually fills every such box with some other value.
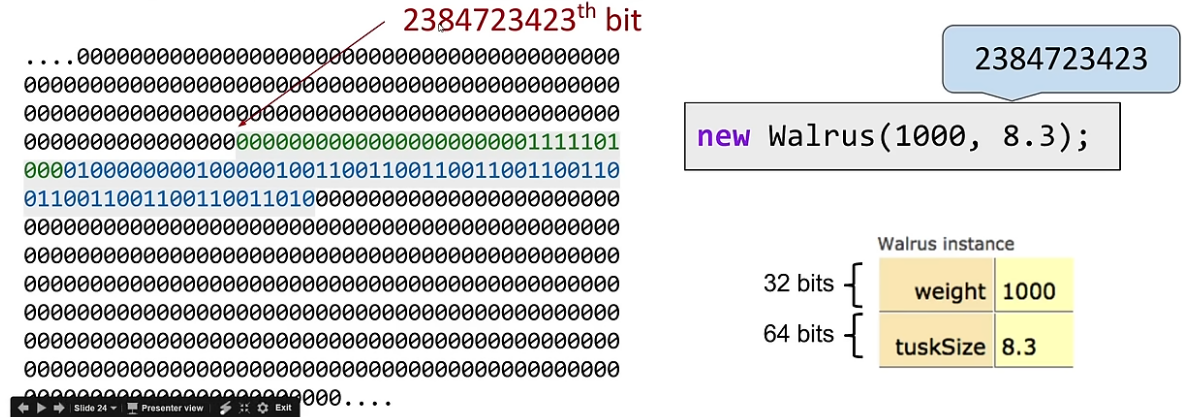
Can think of new as returning the address of the newly created object
- Addresses in Java are 64 bits.
- Example (rough picture): If object is created in memory location
So the
new- allocating memory and returning the address, similar to themallocin C.
Reference Type Variable Declarations
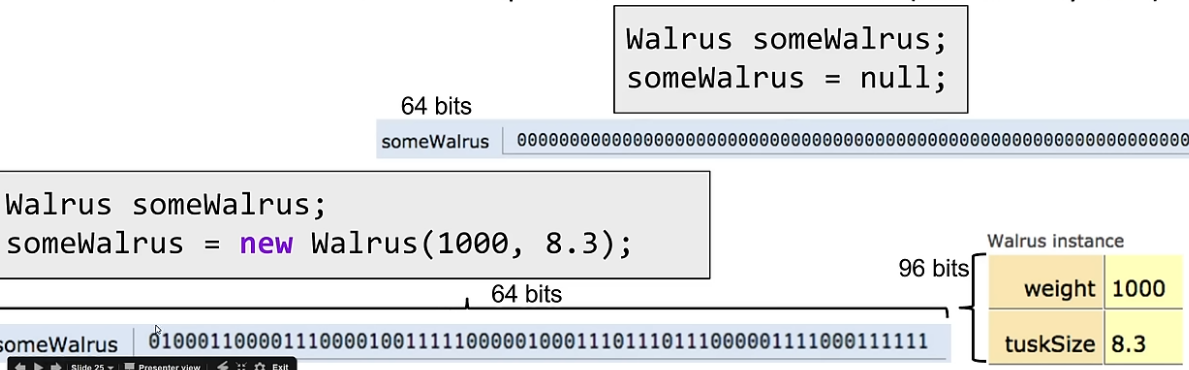
When we declare a variable of any reference type (Walrus, Dog, Planet):
- Java allocates exactly a box of size 64 bits, no matter what type of object.
- These bits can be either set to:
- Null (all zeros).
- The 64 bit “address” of a specific instance of that class (returned by new).
The Golden Rule of Equals(GRoE) (and Parameter Passing)
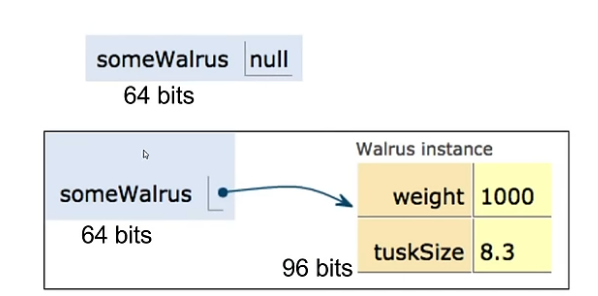
y = x copies all the bits (pass by value) from x into y.
So does reference types, in terms of our visual metaphor, we “copy” the arrow by making the arrow in the b box point at the same instance as a.
Summary
 (Variables that store arrays are reference variables just like any other.)
(Variables that store arrays are reference variables just like any other.)