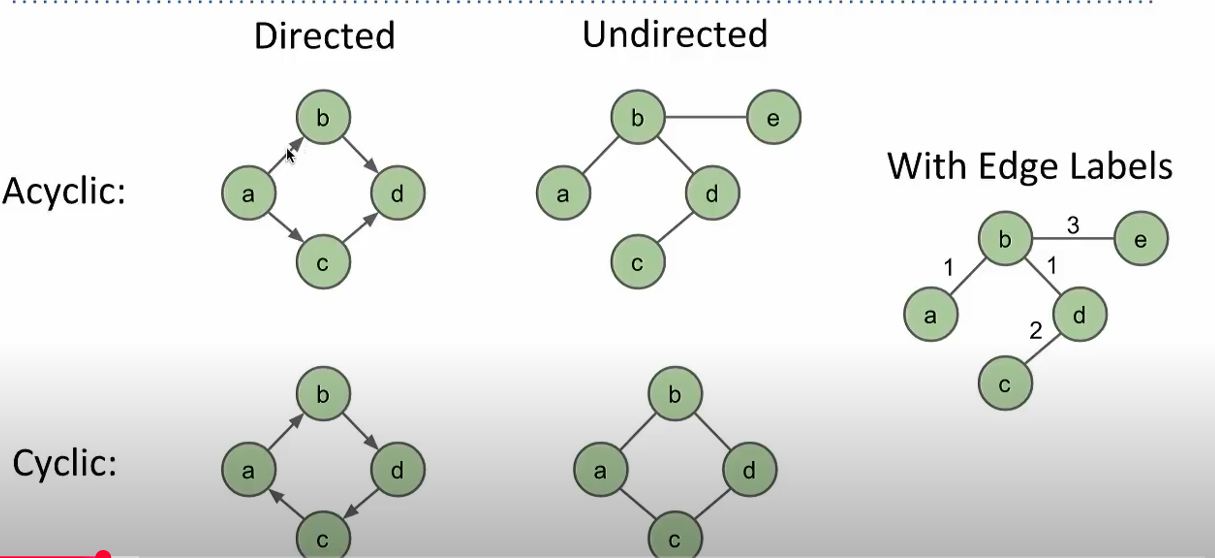
Types
Dense and sparse:


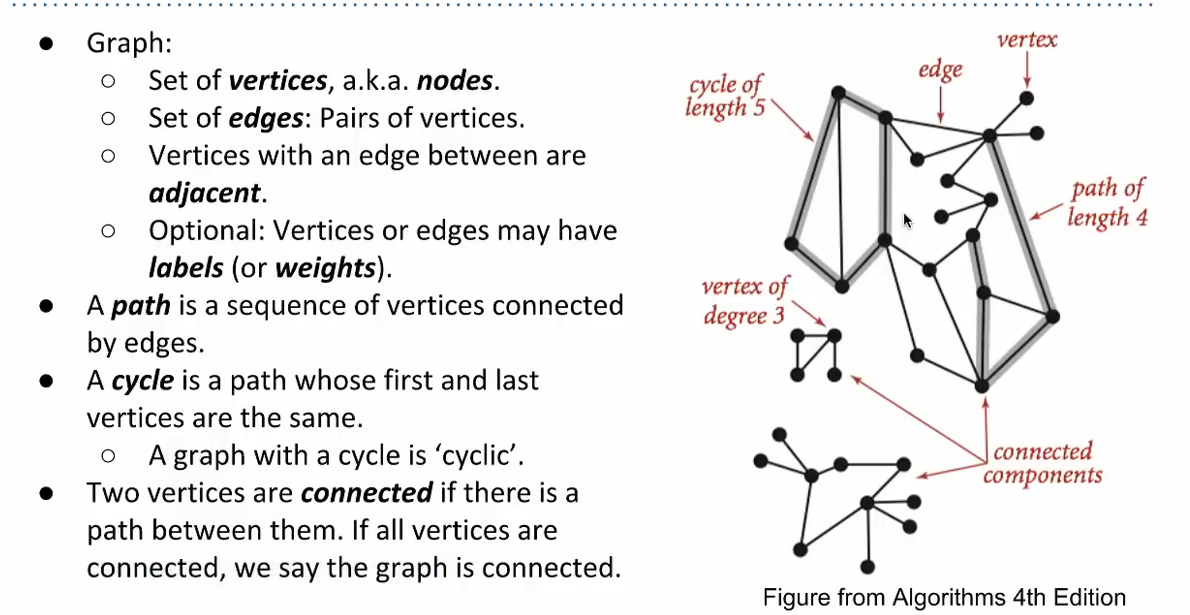
Terminology
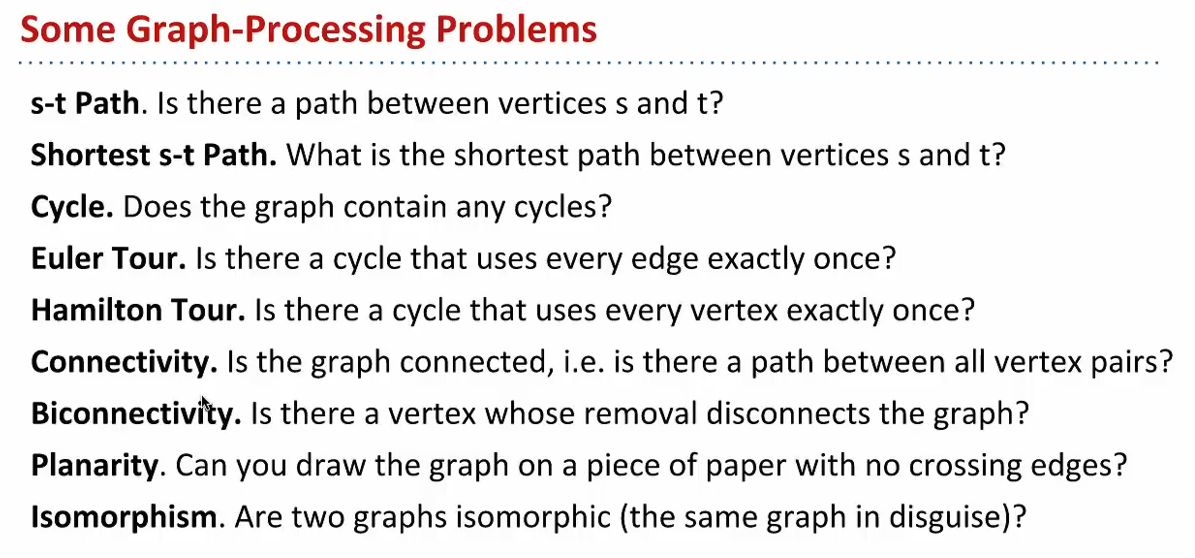
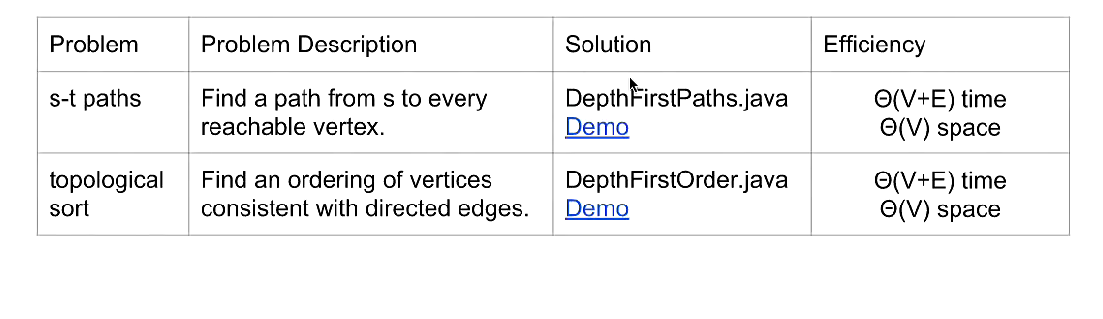
Problems
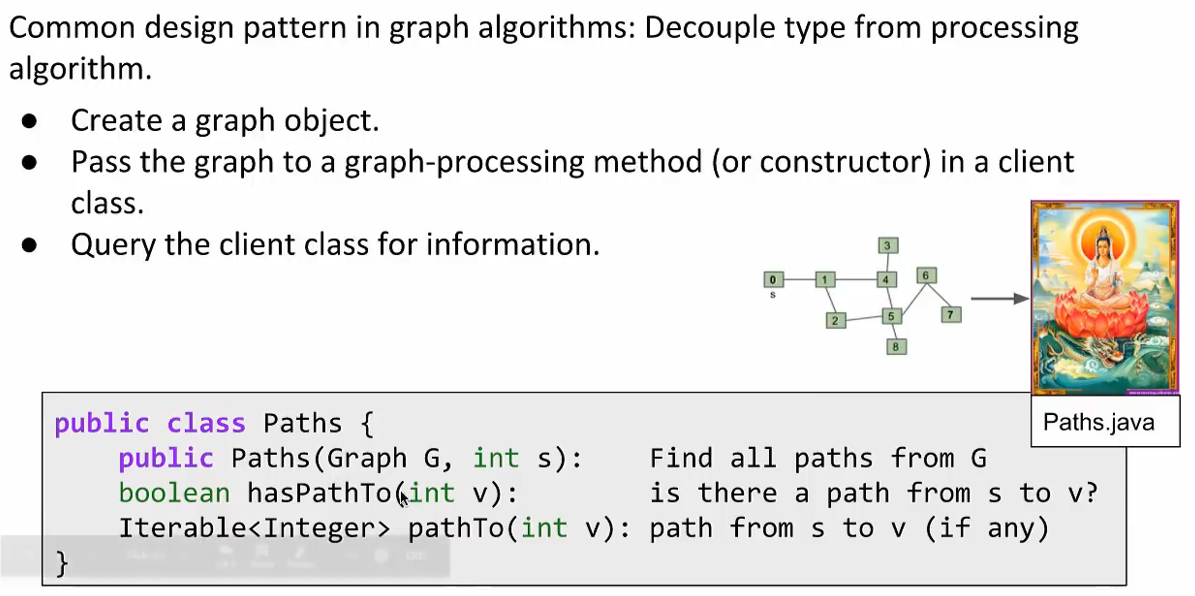
API

Representation
Adjacency Matrix
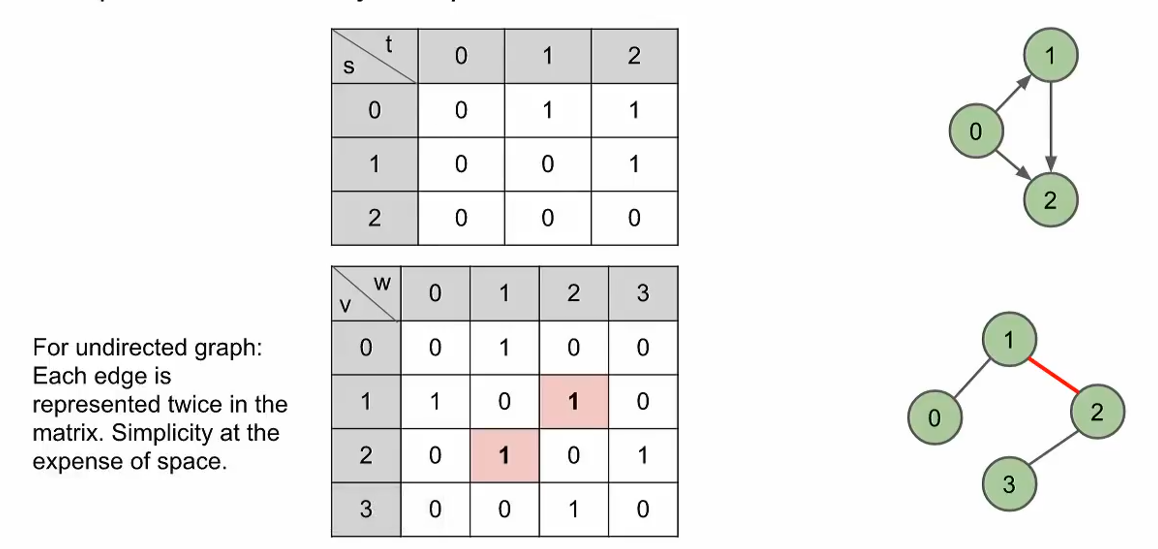
Adjacency List

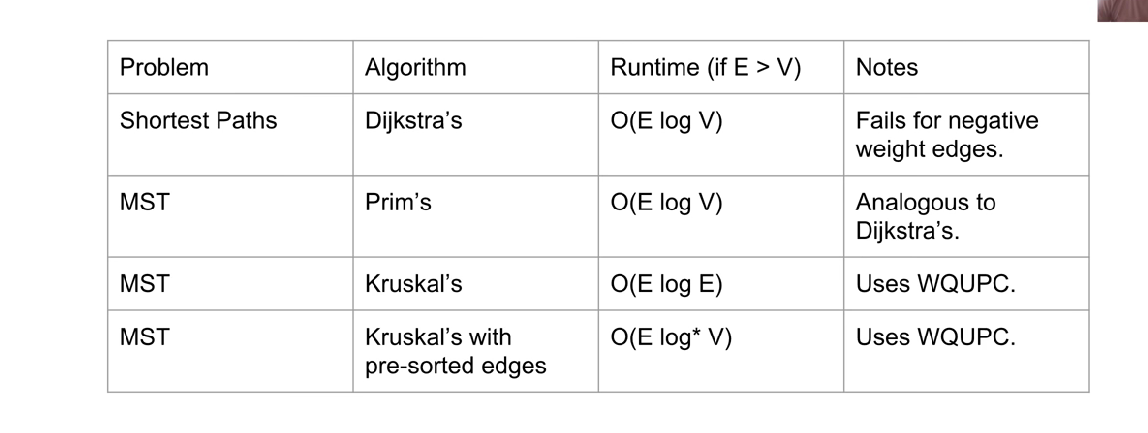
Runtime
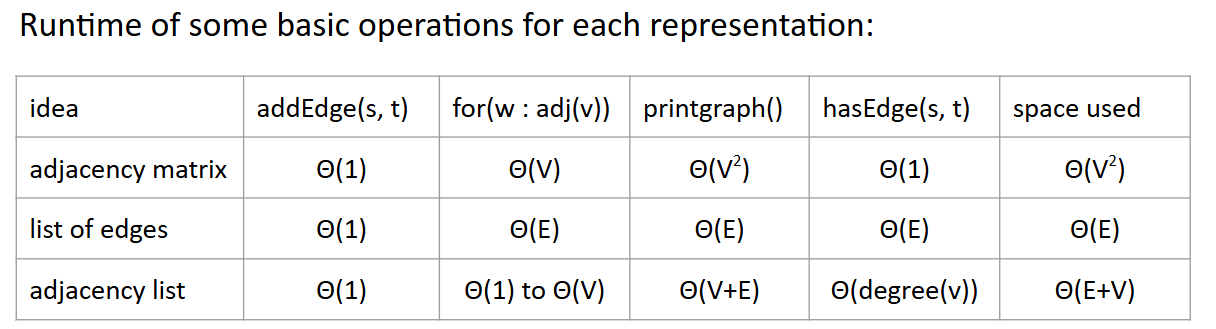 (In fact, the runtime of
(In fact, the runtime of for(w : adj(v)) in adjacency list is theta(E))
Implementation

Traversal
Kinds

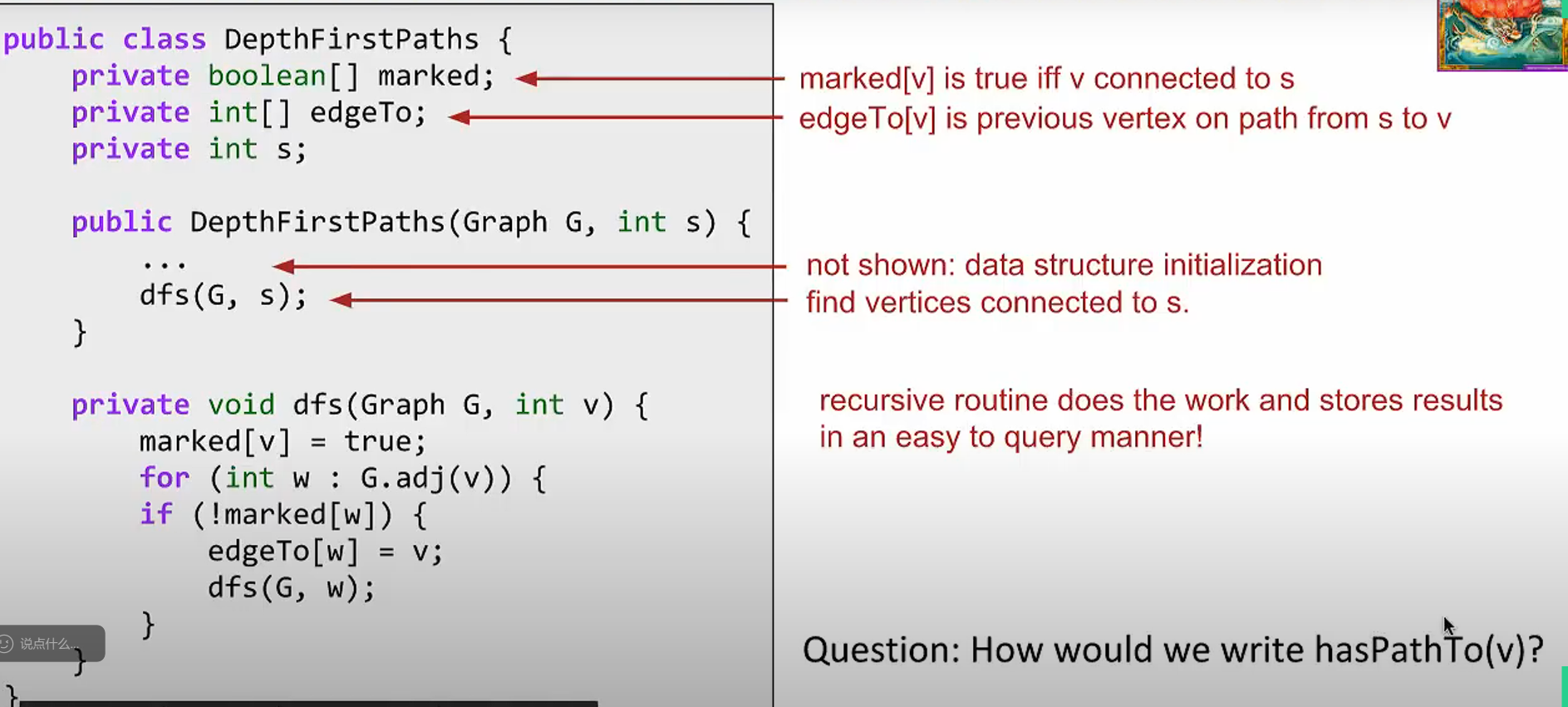
Depth-First



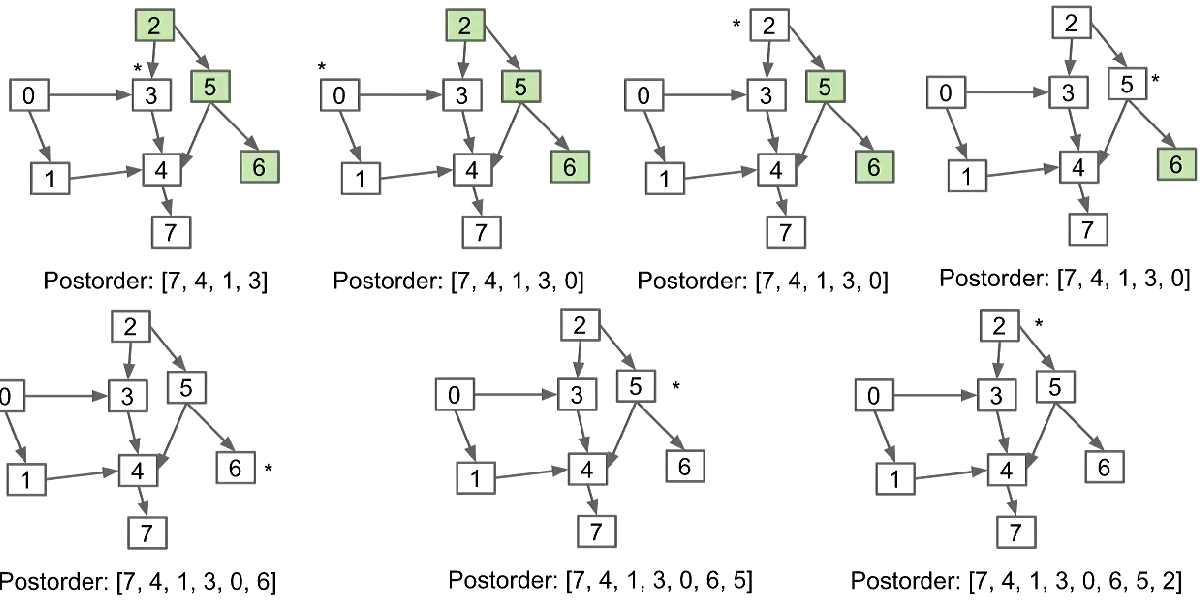
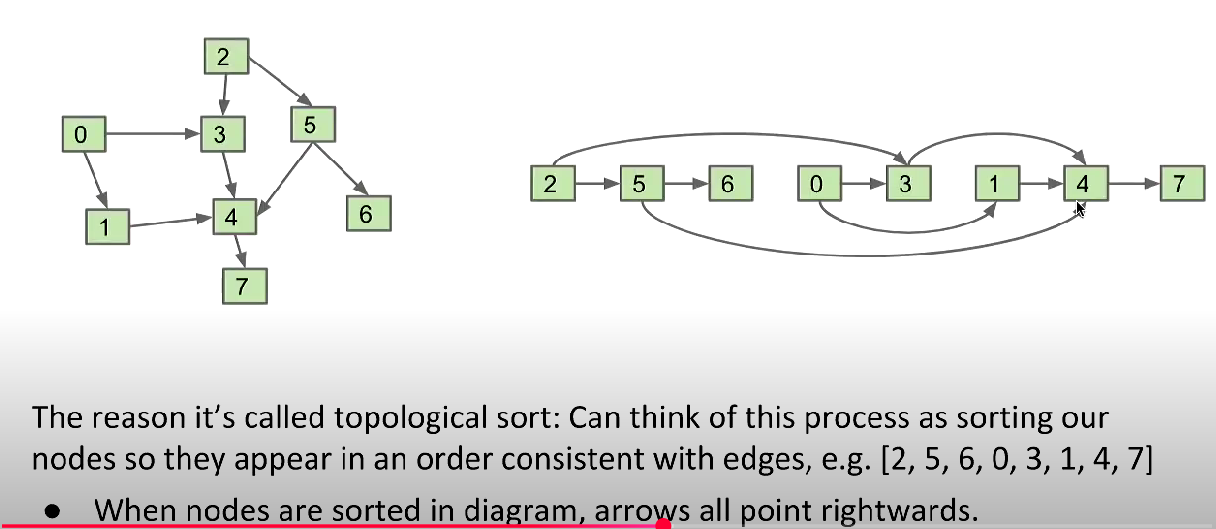
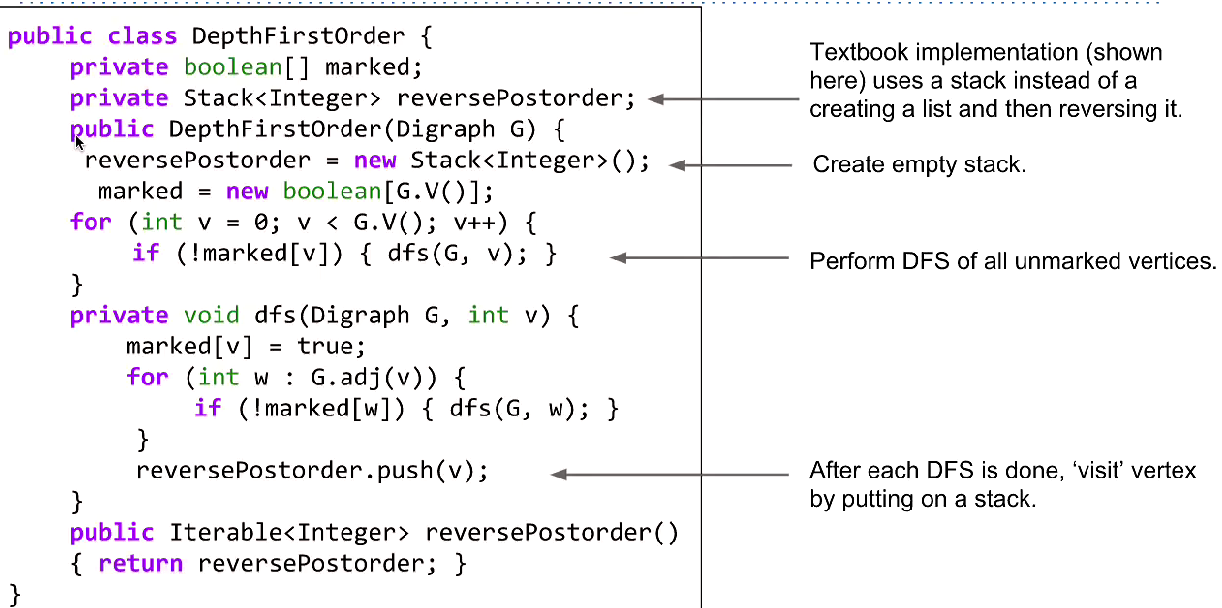
Topological Sort
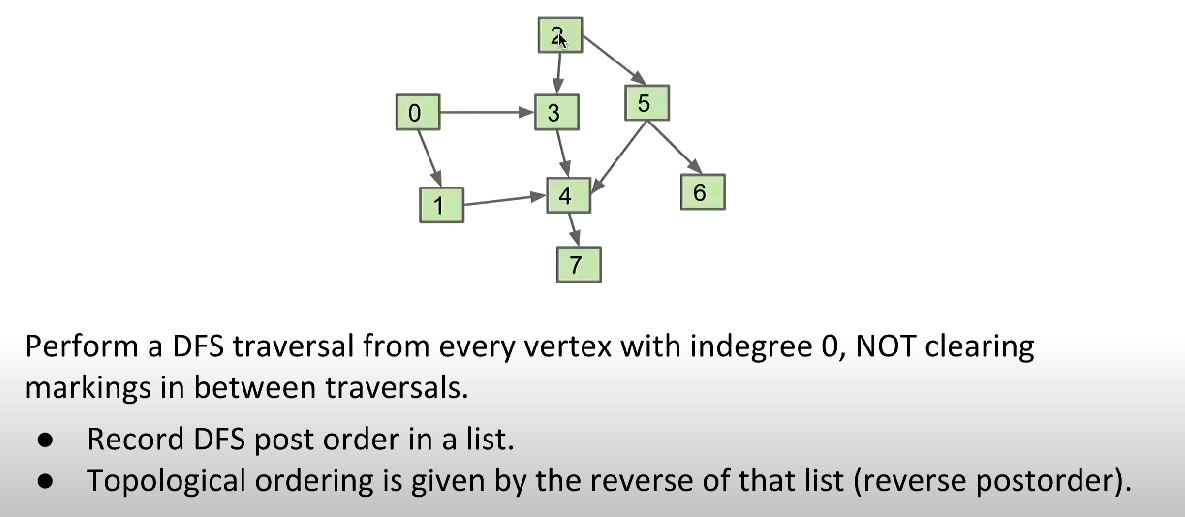 In fact, it’s not a must that start from vertex with indegree 0, it’s OK from any vertex as long as every vertex is visited in the last.
In fact, it’s not a must that start from vertex with indegree 0, it’s OK from any vertex as long as every vertex is visited in the last.
利用 DFS 的「三色标记法」/「递归栈」
我们通常给每个节点维护一个 访问状态,常见的有三种:
- 0 = 未访问(white)
- 1 = 正在访问(在递归栈中)(gray)
- 2 = 已完成访问(black)
具体规则:
- 如果 DFS 到一个未访问的点,就继续递归。
- 如果 DFS 碰到一个「正在访问」的点(即还没回溯完),说明形成了 回边,即有环。
- 如果 DFS 碰到一个「已完成」的点,说明已经拓扑排序过了,直接跳过。
Example:
 方法二:Kahn 算法
4. 初始化:计算所有顶点的入度,将入度为 0 的顶点加入队列(作为起点)。
5. 迭代:从队列中取出一个入度为 0 的顶点,将其加入排序结果;然后减少其所有邻接顶点的入度,若邻接顶点入度变为 0,则加入队列。
6. 重复步骤 2,直至所有顶点被处理(若图中存在环,则无法完成排序)。
方法二:Kahn 算法
4. 初始化:计算所有顶点的入度,将入度为 0 的顶点加入队列(作为起点)。
5. 迭代:从队列中取出一个入度为 0 的顶点,将其加入排序结果;然后减少其所有邻接顶点的入度,若邻接顶点入度变为 0,则加入队列。
6. 重复步骤 2,直至所有顶点被处理(若图中存在环,则无法完成排序)。
 Not a ordering sort like quick sort.
Not a ordering sort like quick sort.
Implementation
Comparison
Breadth-First
 Handy for finding shortest paths.
Handy for finding shortest paths.
Implementation

The Shortest Path
We will get a tree which contains the shortest way to every reachable vertex from source.
The Dijkstra Algorithm
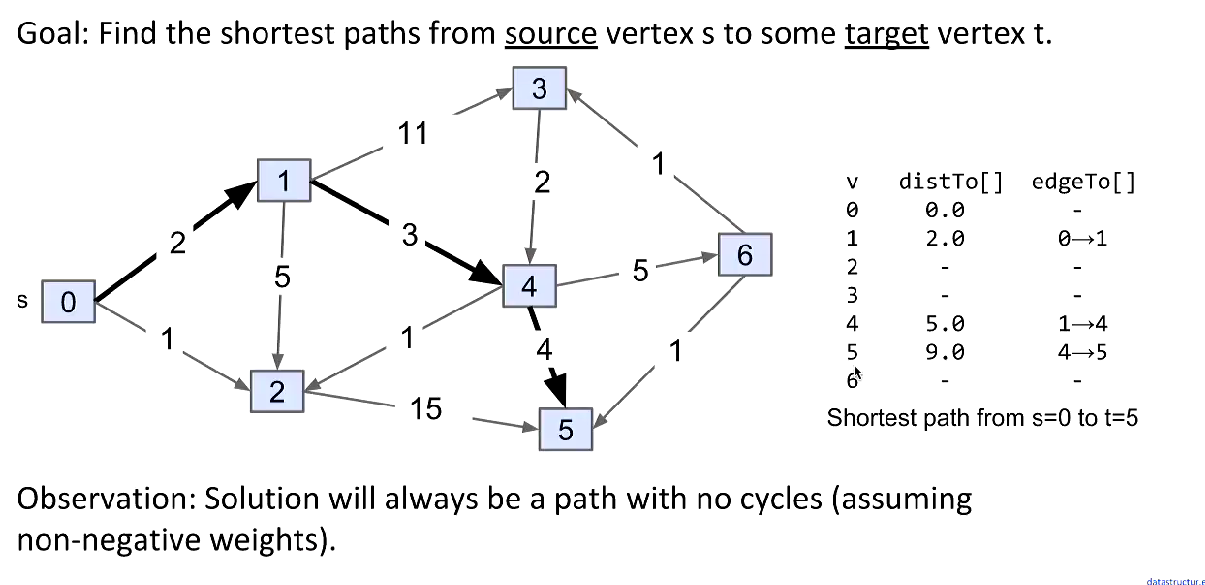 If there’s a graph with V vertices and w edges and every vertex is reachable, there will be V-1 edges in the shortest path tree.
If there’s a graph with V vertices and w edges and every vertex is reachable, there will be V-1 edges in the shortest path tree.
Implementation
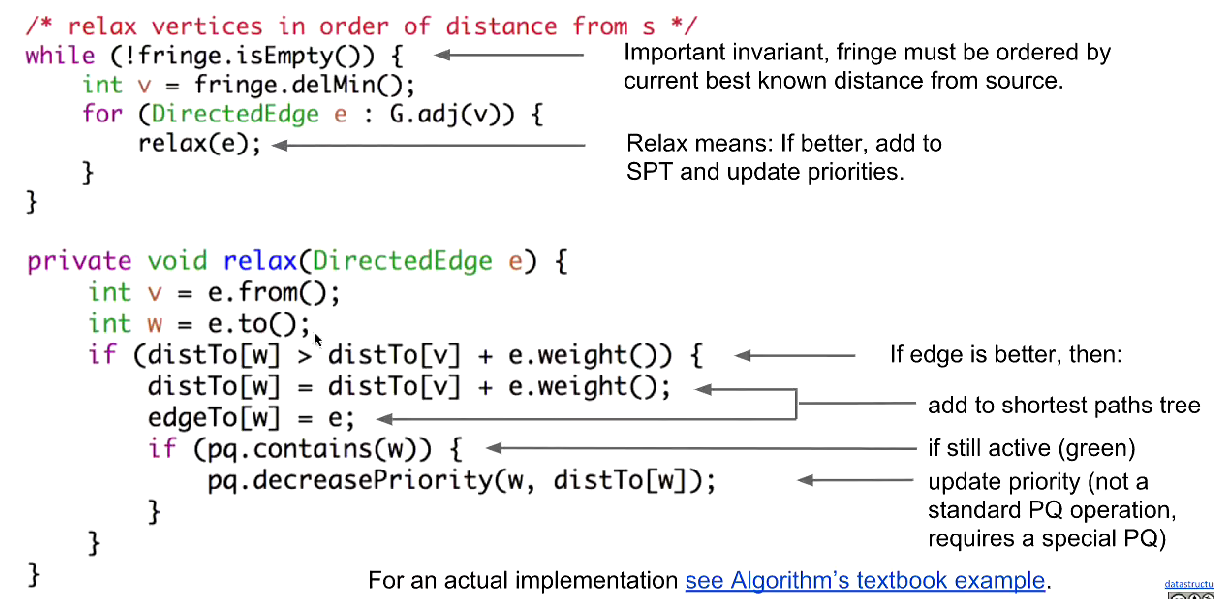
Relaxation:
Use it if better.
松弛操作指的是:对于图中的一条边 (u, v)(从节点u到节点v),如果当前已知从起点到v的距离,大于 “从起点到u的距离 + 边(u, v)的权重”,则更新 “起点到v的距离” 为后者。
简单说,就是检查是否能通过中转节点u,找到一条到v的更短路径,如果可以就更新路径长度。
例如:
- 假设当前起点到
v的距离是 10, - 起点到
u的距离是 3,边u→v的权重是 5, - 那么通过
u到v的总距离是 3+5=8,小于 10,此时就 “松弛” 这条路径,将起点到v的距离更新为 8。
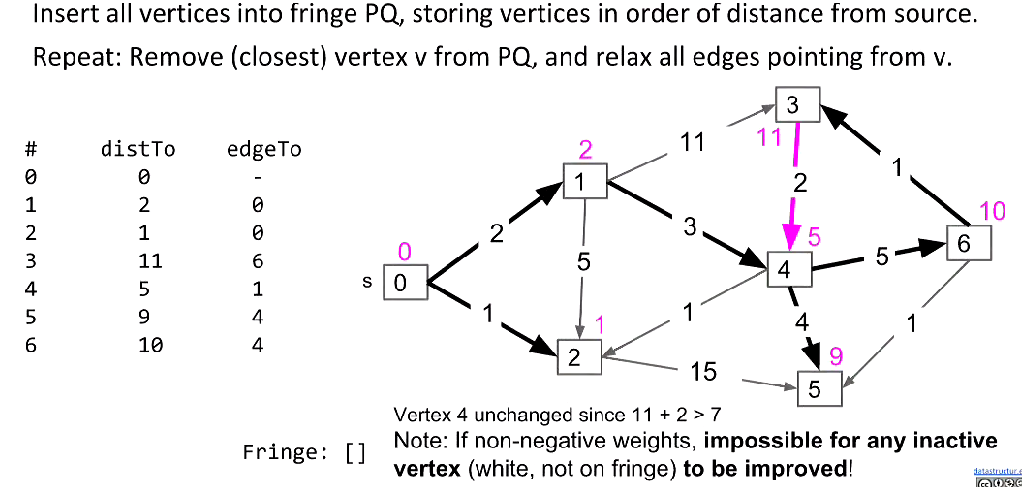
Best-First
Visit vertices in order of best-known distance from source, relaxing each edge from the visited vertex.
If a node is selected by best-first and added in the result array, it will never be changed.
Fringe(PQ)
Maintain a heap(PQ) to find the closest vertex, so that we will not waste our time to search for distTo array.
Pseudocode

 (pq is fringe)
(pq is fringe)
Runtime
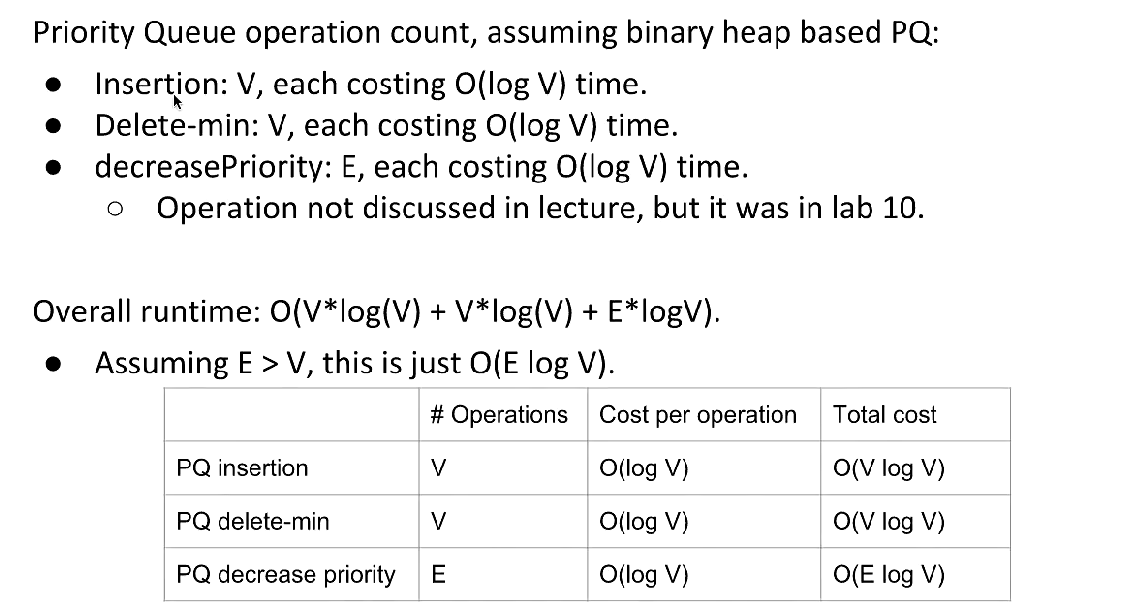
 也就是说,对于松弛操作,由于更改距离后要维护堆,堆优化的时间从E变成了Elog(V),因此对于稠密图,松弛次数多,会浪费时间。
也就是说,对于松弛操作,由于更改距离后要维护堆,堆优化的时间从E变成了Elog(V),因此对于稠密图,松弛次数多,会浪费时间。
Navigation(A*)
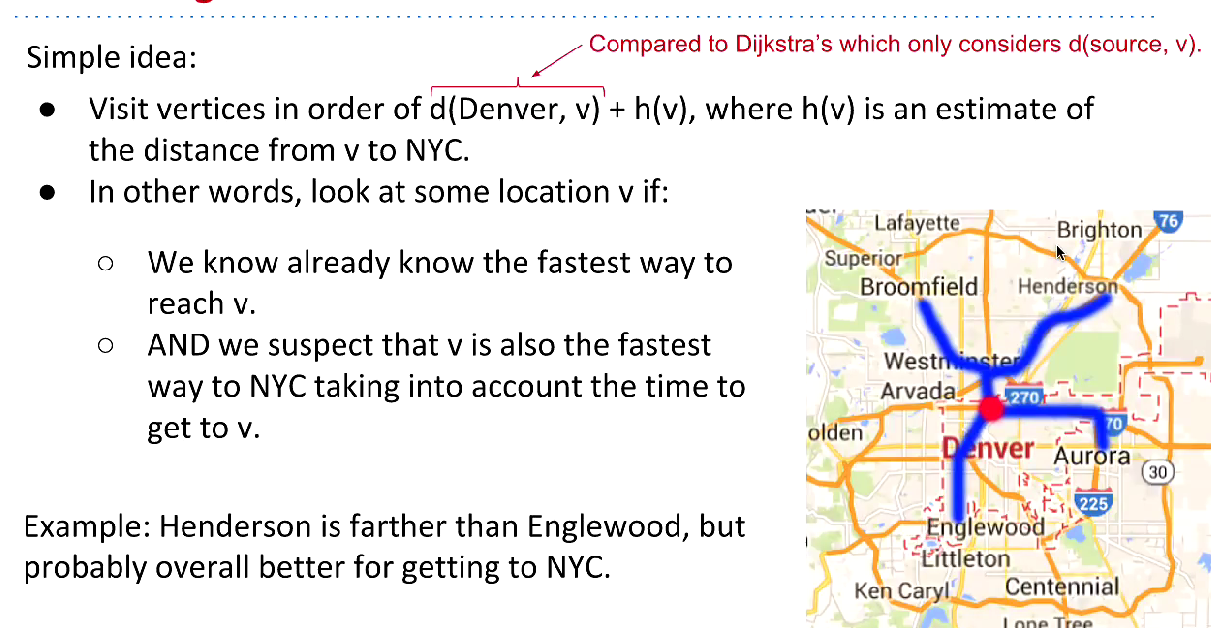
 In this example, we can use the straight distance between two city as
In this example, we can use the straight distance between two city as h.
It does not change the algorithm but use h + distTo instead of only dist.
Wrong heuristic will lead to wrong path.
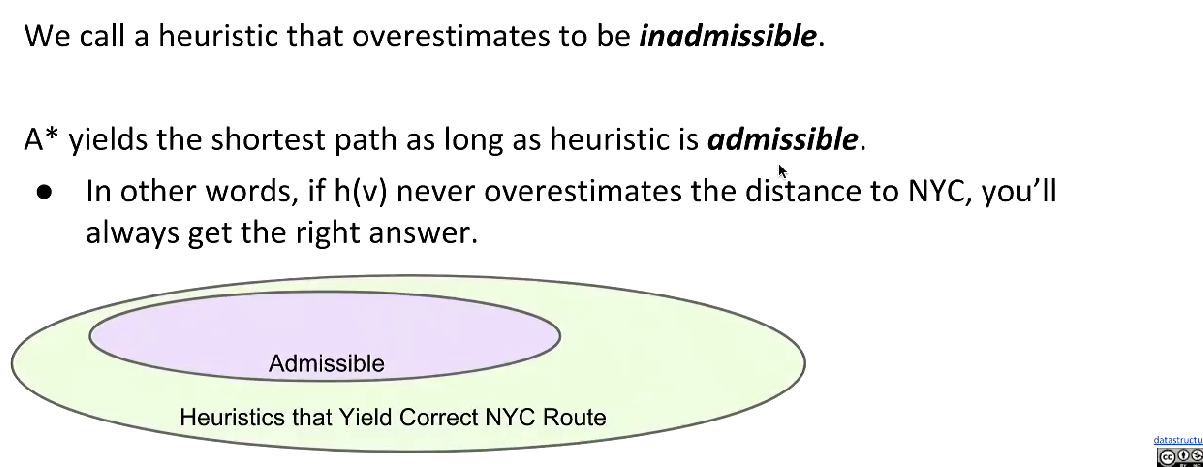 So we should set
So we should set h(v) <= actual distance from v to destination


The Minimum Spanning Trees
Cycle:
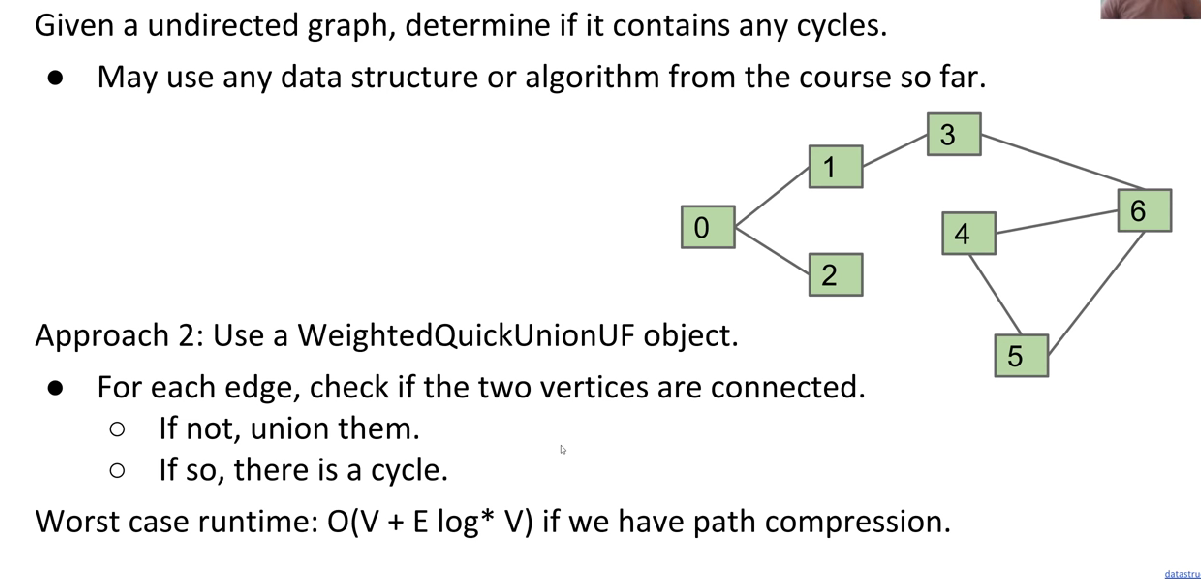 See in Kruskal
See in Kruskal
Definition
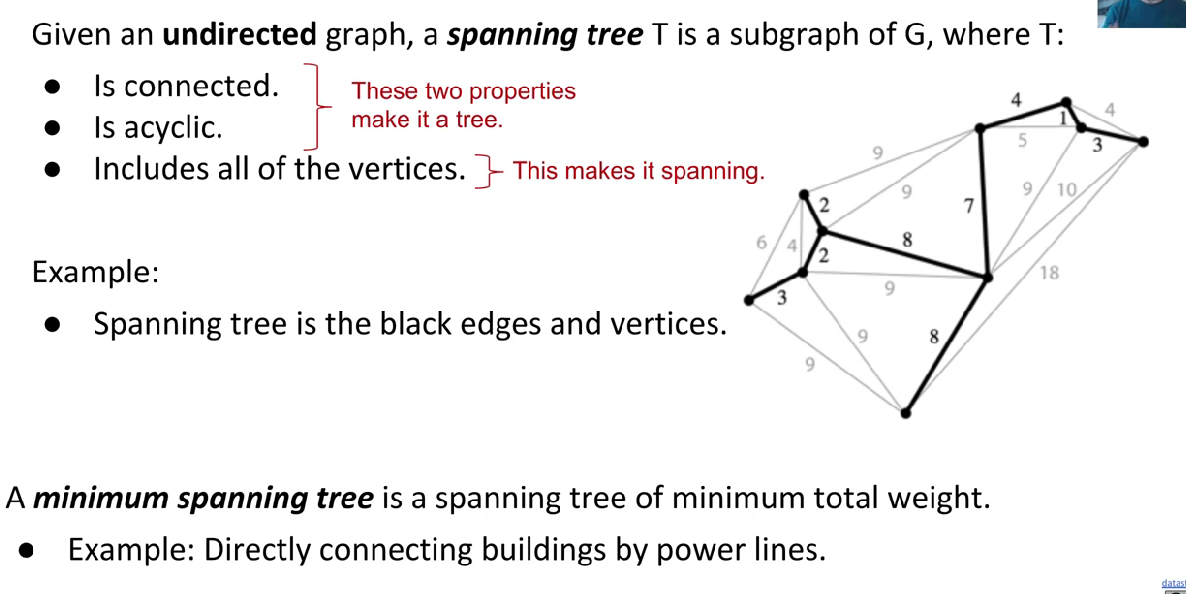
MST VS SPT

Implementation
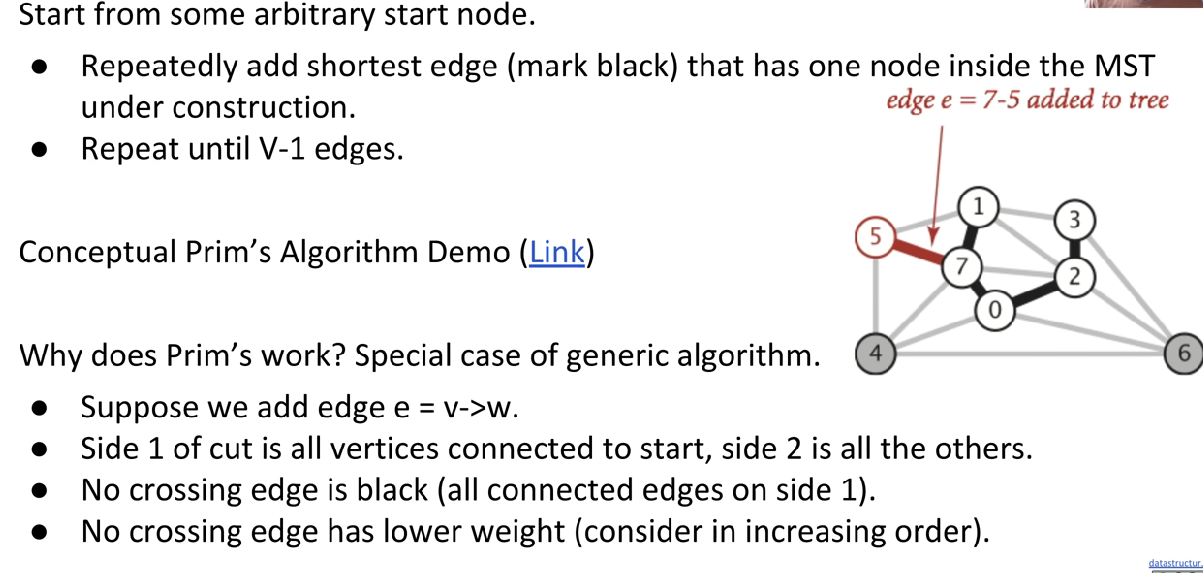
Prim’s Algorithm
Cut Property
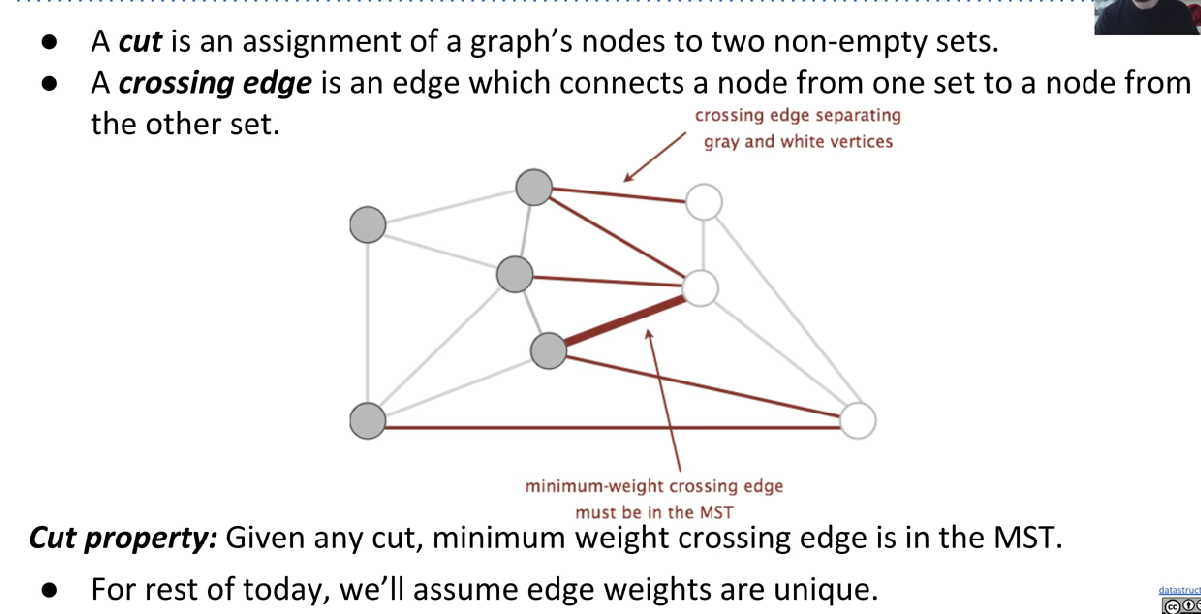 Proof:
Proof:
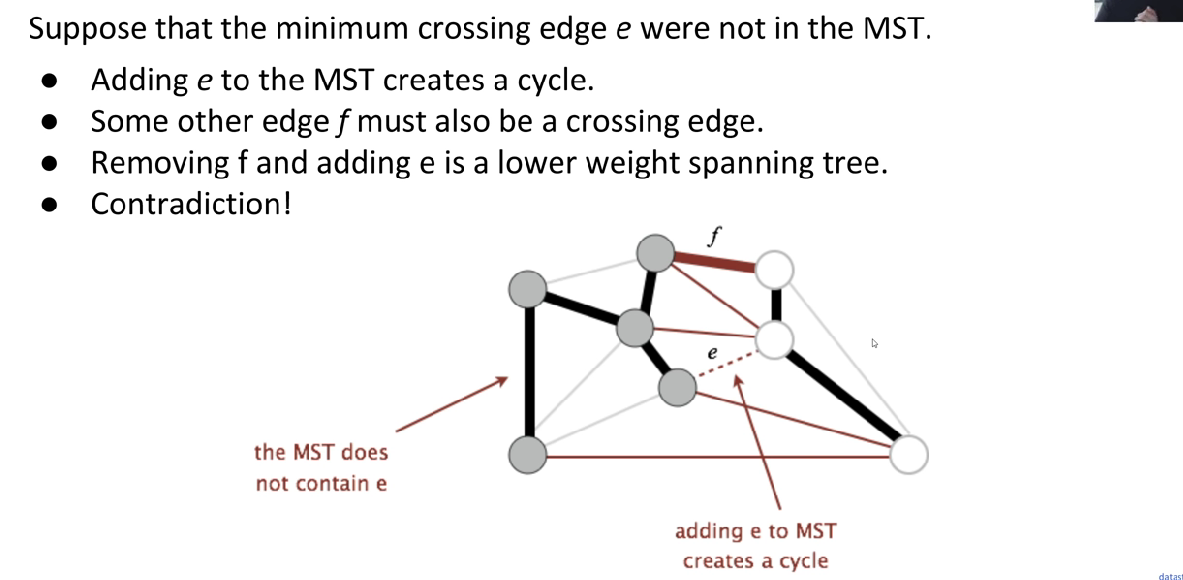
 (According to cut property, if there’s cross edges with same weight, at least one in the MST, and maybe MST is not unique.)
(According to cut property, if there’s cross edges with same weight, at least one in the MST, and maybe MST is not unique.)
Improvement: PQ
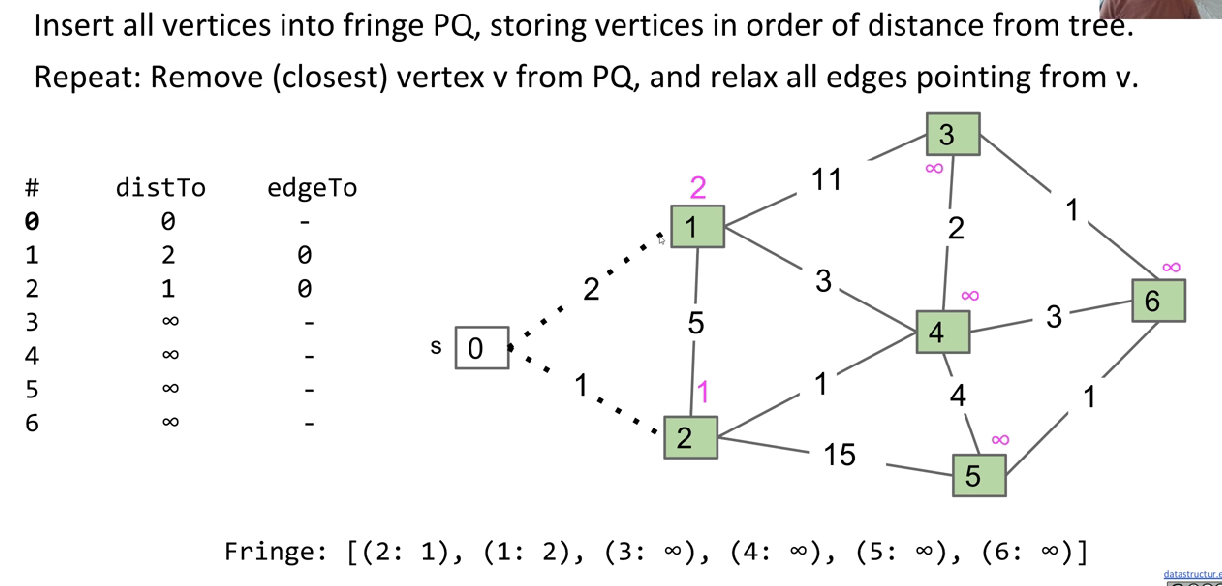
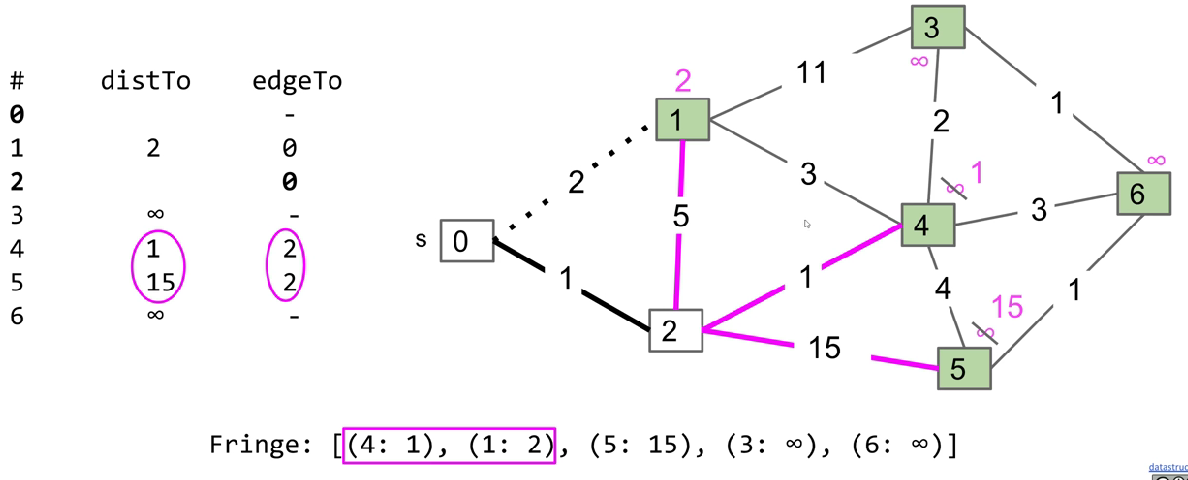
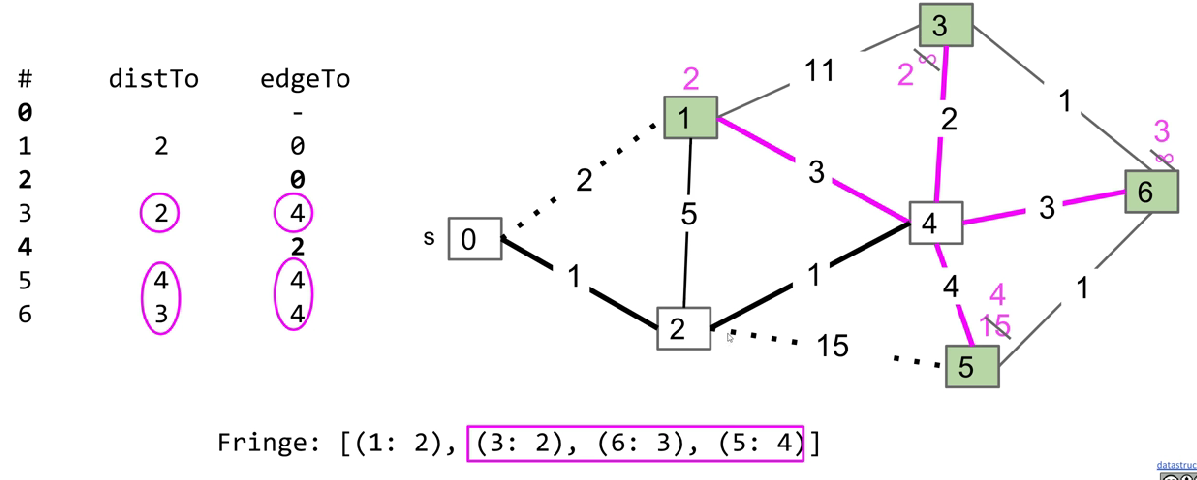
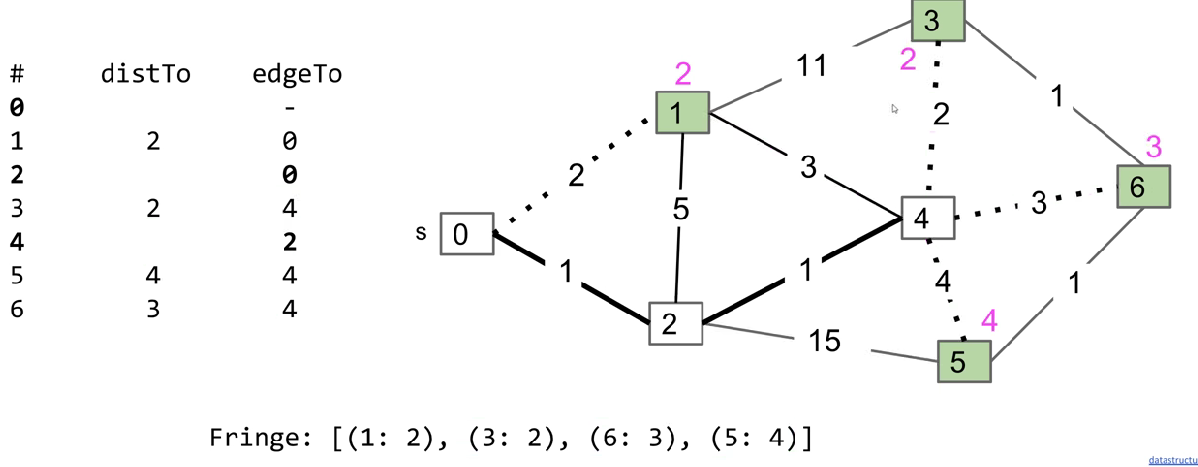
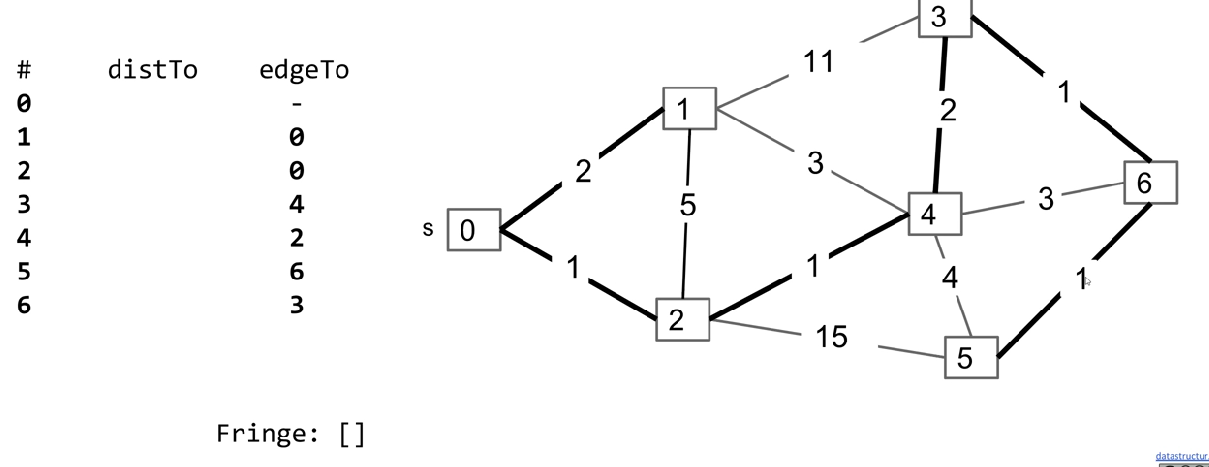 So that we can consider less edges possible to be added.
So that we can consider less edges possible to be added.
Comparison:



Pseudocode

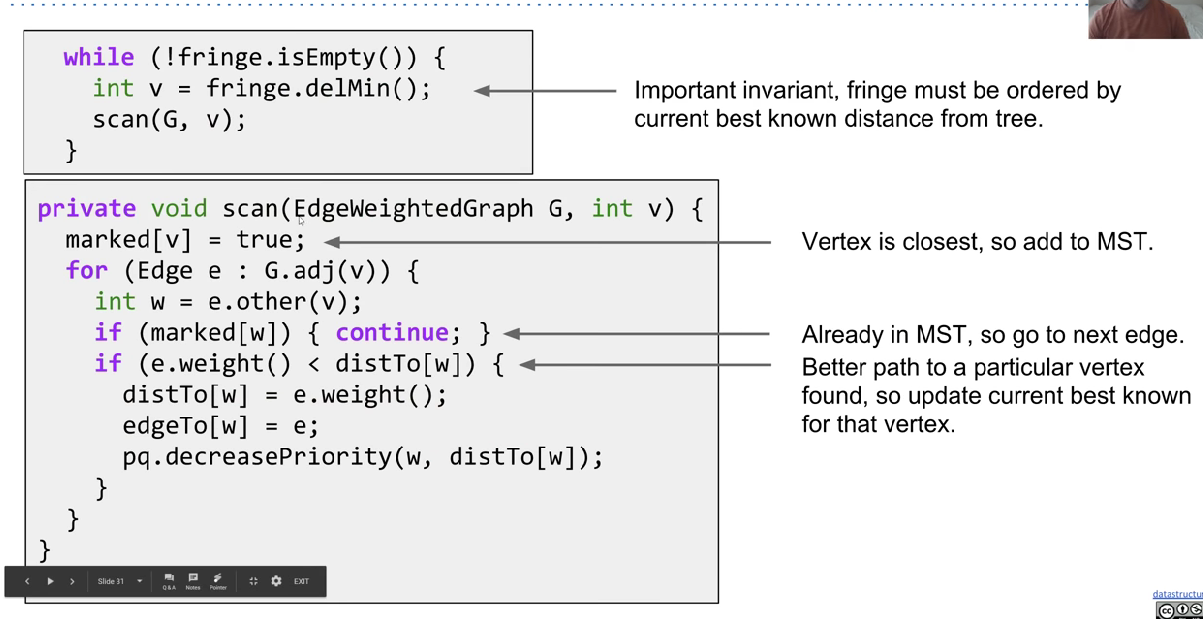
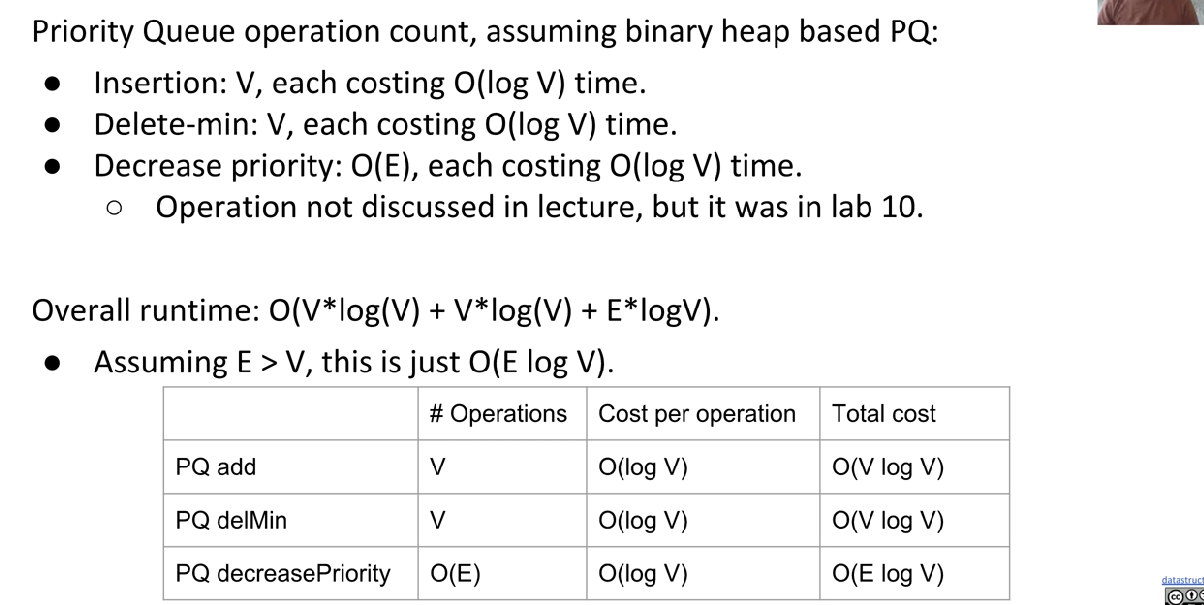
Runtime
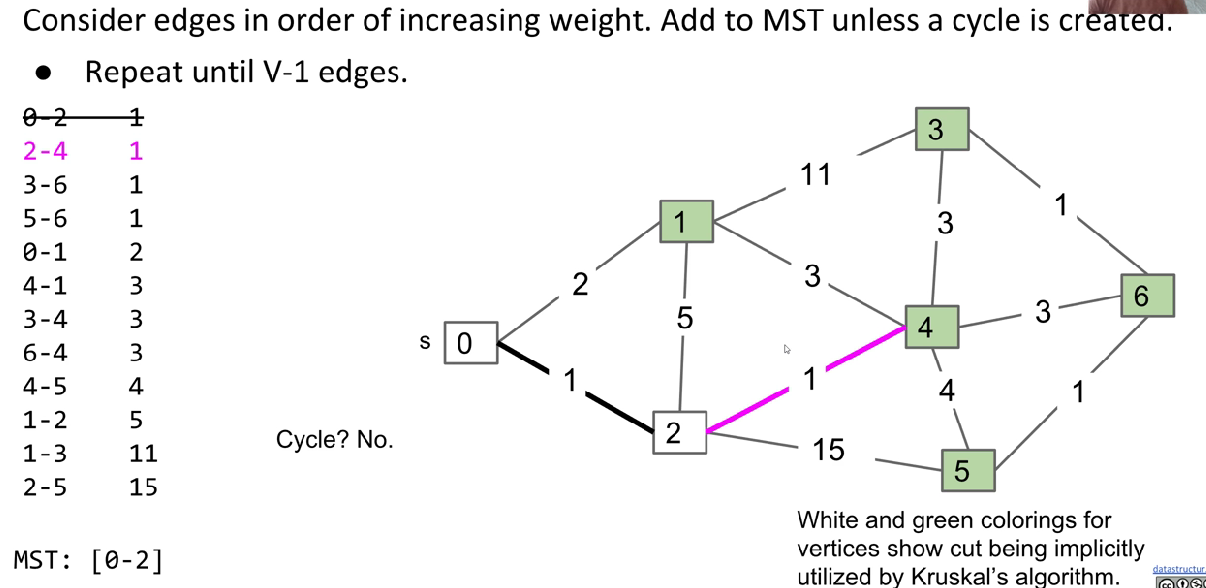
Kruskal’s Algorithm
 Data structure: PQ, WQU
Data structure: PQ, WQU
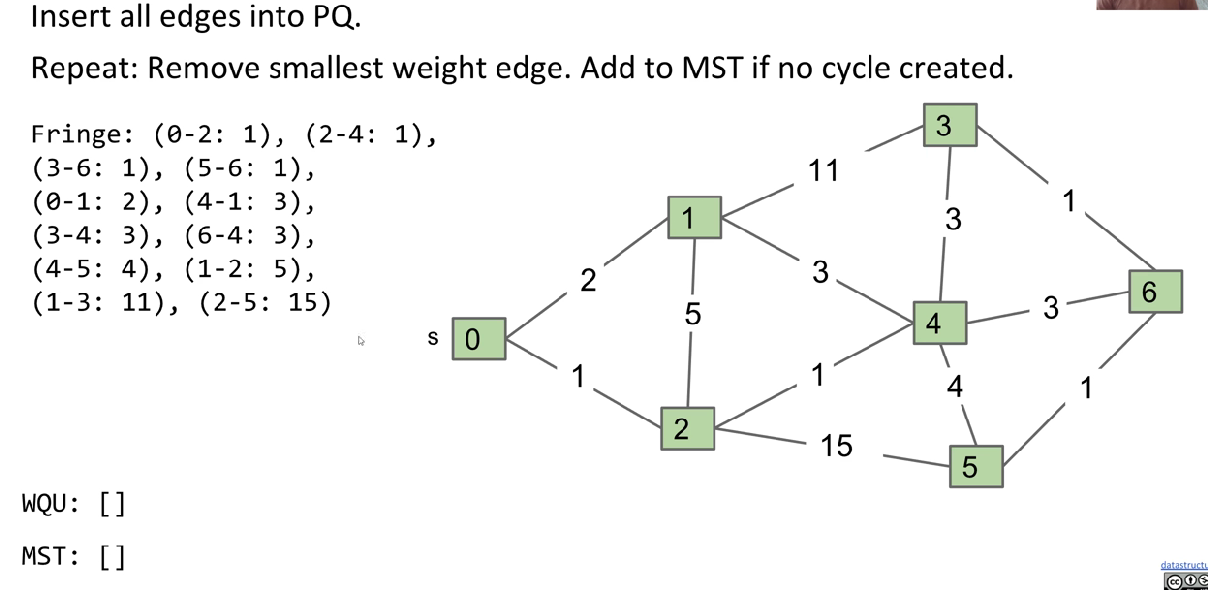
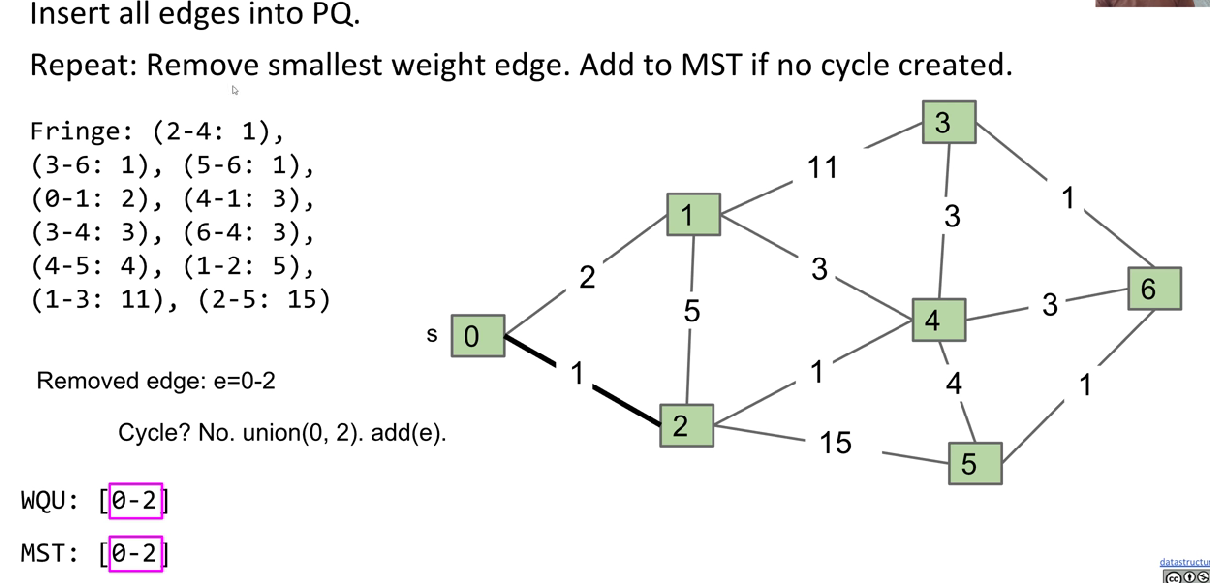
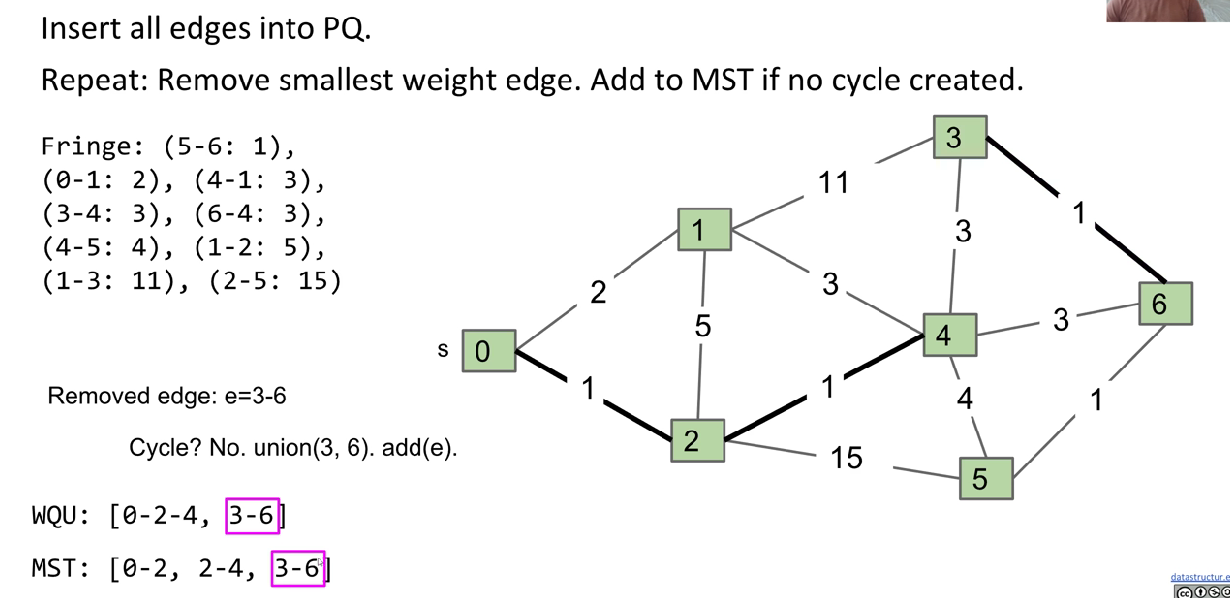
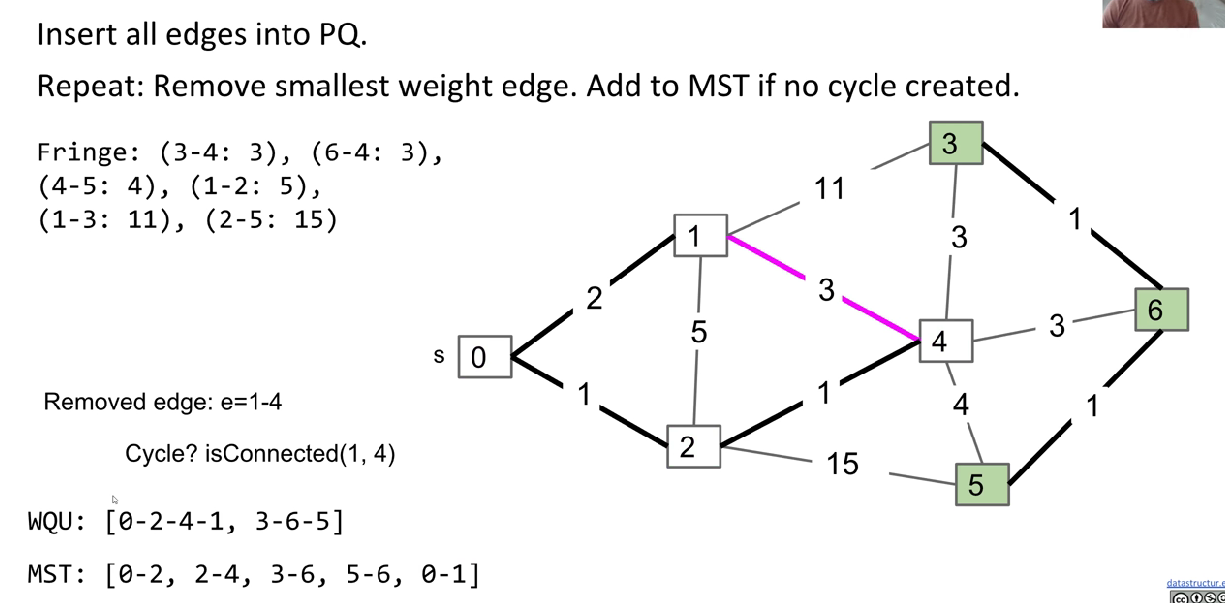
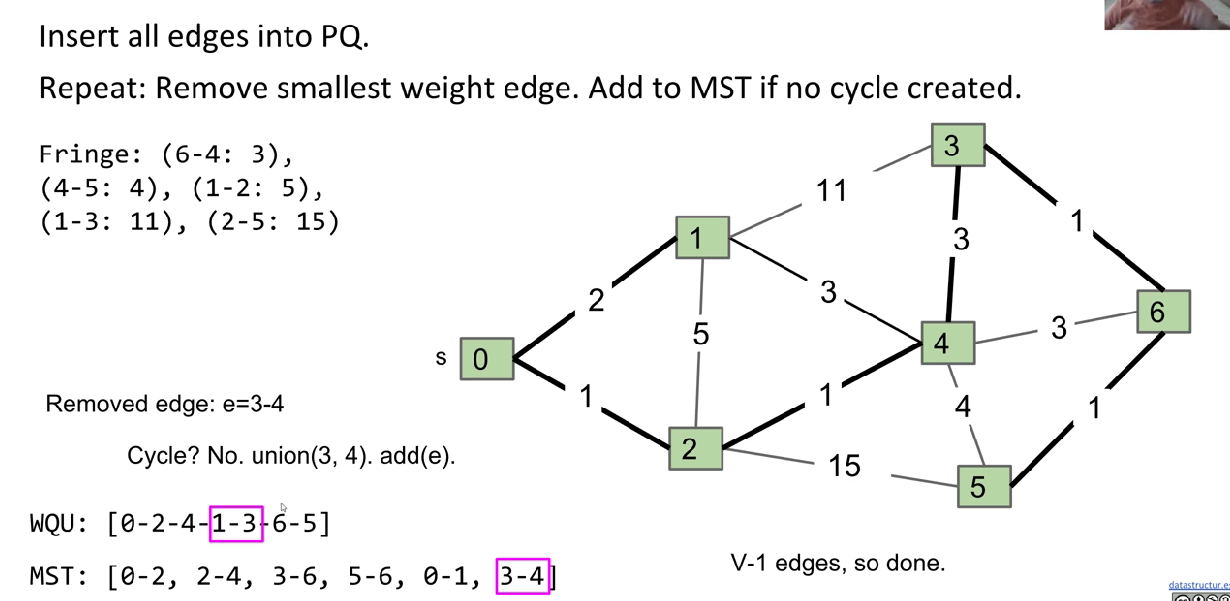
Principle:

Pseudocode

Runtime
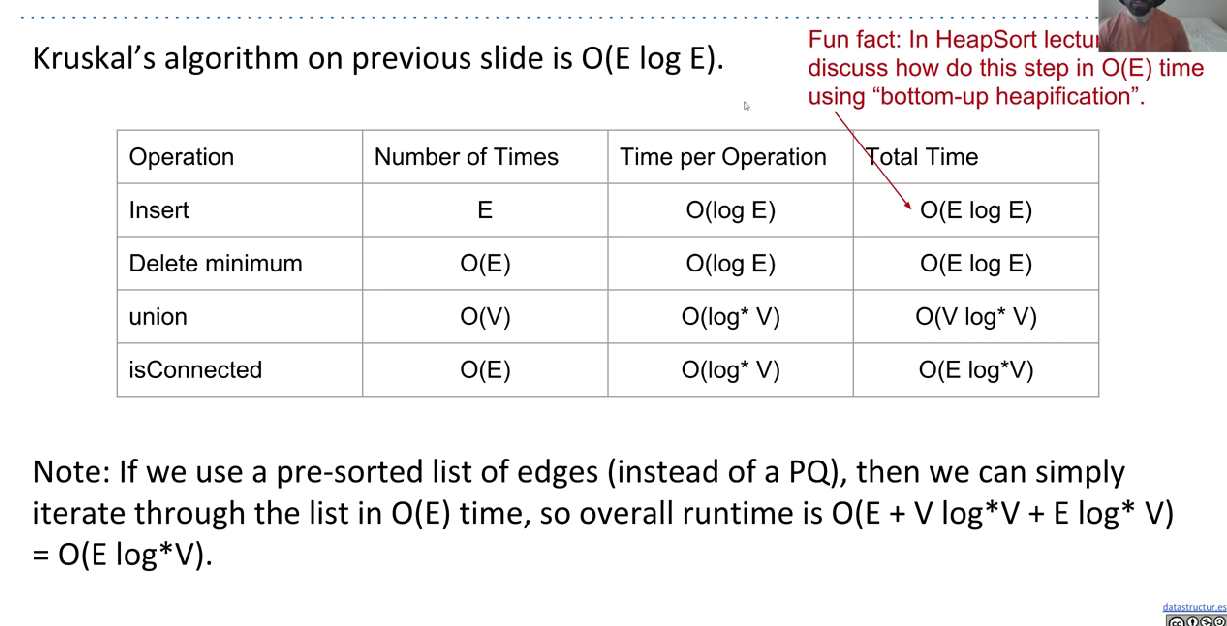
Summary