An optimization method for Functional Programming.
We can eliminate the frames we do not need in a recursive call so that we can finish computation in constant space.
 Those frame all return a same value, the value returned by the last frame.
Those frame all return a same value, the value returned by the last frame.
So these middleman are useless after they executed a recursive call.
Tail Call
When have a recursive call, distinguish whether the function has other things to do, or the last thing is just return the value of recursion.
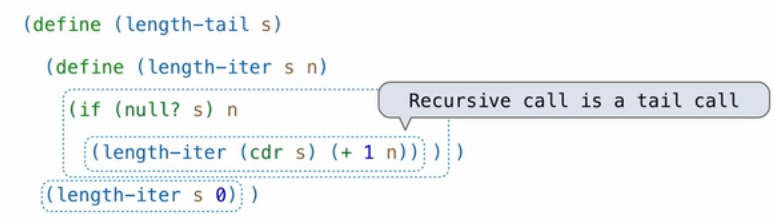
A procedure call that has not yet returned is active. Some procedure calls are tail calls. A Scheme interpreter should support an unbounded number of active tail calls using only a constant amount of space.
A tail call is a call expression in a tail context:
- The last body sub-expression in a
lambdaexpression - Sub-expressions 2(consequent) & 3(alternative) in a tail context
ifexpression - All non-predicate sub-expressions in a tail context
cond - The last sub-expression in a tail context
andoror - The last sub-expression in a tail context
begin
A call expression is not a tail call if more computation is still required in the calling procedure.
But linear recursive procedures can often be re-written to use tail calls.

Map and Reduce
(define (reduce procedure s start)
(if (null? s) start
(reduce (cdr s) (procedure start (car s)))
)
)Recursive call is a tail call.
Other calls are not; constant space depends on whether procedure requires constant space.